What are tides?
They are a natural phenomenon observed mainly along the coasts, with varying degrees of intensity. They are the continuous, daily movement of water masses, whose levels alternately rise and fall in the same location.
Tides: How do they work?
This perpetual motion is caused by the attraction of the sun, the moon, and the mass of water on the globe. The masses attract each other to a greater or lesser extent depending on the respective positions of the three celestial bodies. The moon is the main driver of the tide.
The tide is the most visible phenomenon on Earth due to the impact of the moon. Since it is an astronomical phenomenon, tides can be predicted. This is known as prediction.
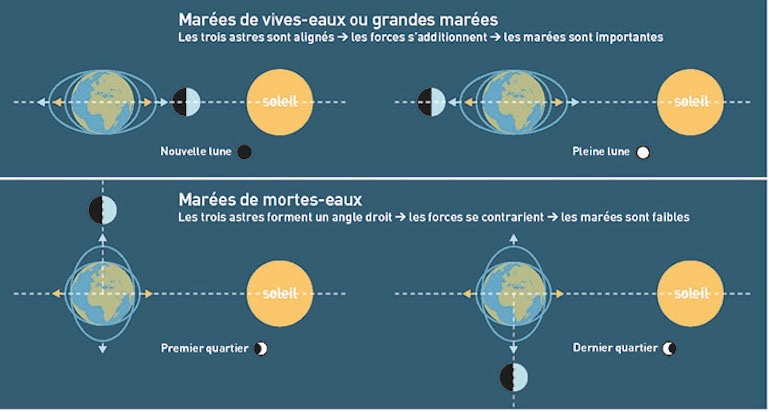
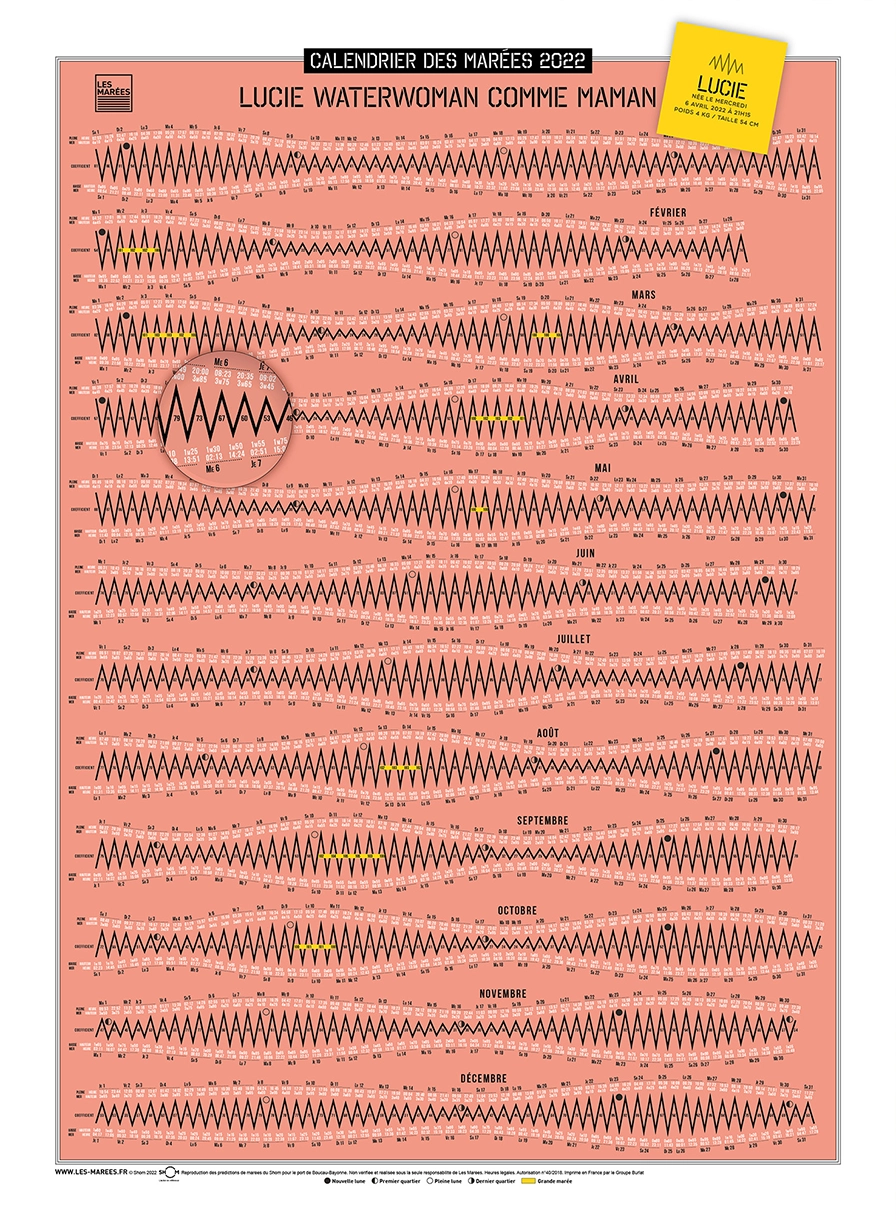
Translation of the visual :
Marées de vives-eaux means spring tides.
Marées de mortes-eaux means Neap tides.
Nouvelle lune (new moon), plaine lune (full moon), premier quartier (first quarter) and dernier quartier (last quarter)
Sensitive to the moon? Download our free calendrier lunaire 2025.
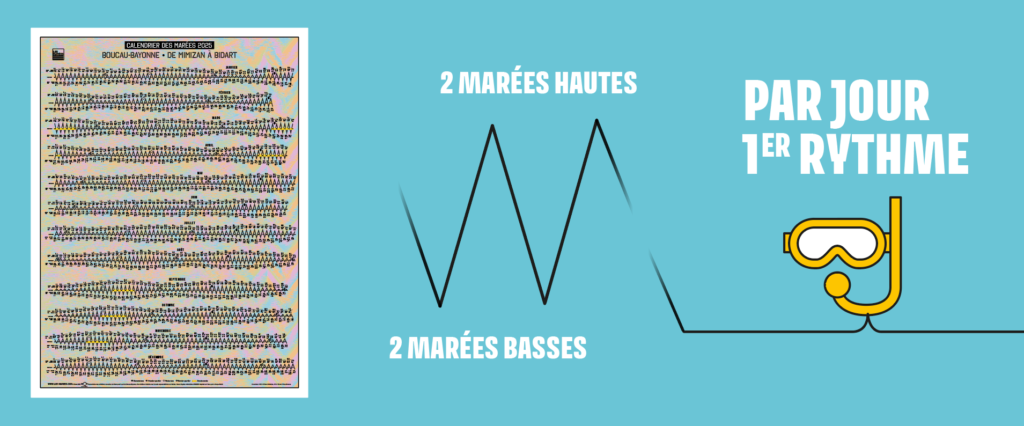
How many tides per day ?
This is the first and easiest rhythm to observe.
The water rises or falls four times a day:
- 2 high tides (marées hautes)
- 2 low tides (marées basses)
To simplify, in a 24-hour day, the water rises in about 6 hours and falls in about 6 hours.
Note that this is only a guideline, as in reality this time frame is never exactly 6 hours. It could be more or less.
This initial rhythm is due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis every 24 hours and the Moon’s movement around the Earth every 24 hours and 50 minutes.
The difference between the 24-hour solar day and the 24-hour and 50-minute lunar day also explains why, at least 4 times a month, there are only 3 tides per day (instead of 4).
Therefore, four times a month:
- There are only two high tides and one low tide, or
- There are only one high tide and two low tides
When the second tide of the day occurs around noon, the “fourth” tide occurs the following day.
What is the daily tide time difference?
The lunar day causes a shift in time from day to day of an average of 50 minutes at the same location along the coast.
Again, this is only an average, as in reality, the tide, which is at 6:00 a.m., will not be exactly at 6:50 a.m. the next day.
The shift can be as much as 35 minutes or as much as an hour from one day to the next.
Is the rate of rise and fall of the water regular?
No, the tide rises and falls in stages. Its movement is irregular.
This is important to know for safety reasons, especially on coasts where the tidal range is significant.
Be careful at mid-tide, where the speed accelerates!
You may be surprised by the speed of the rising water, given that the sea generally rises faster than it falls.
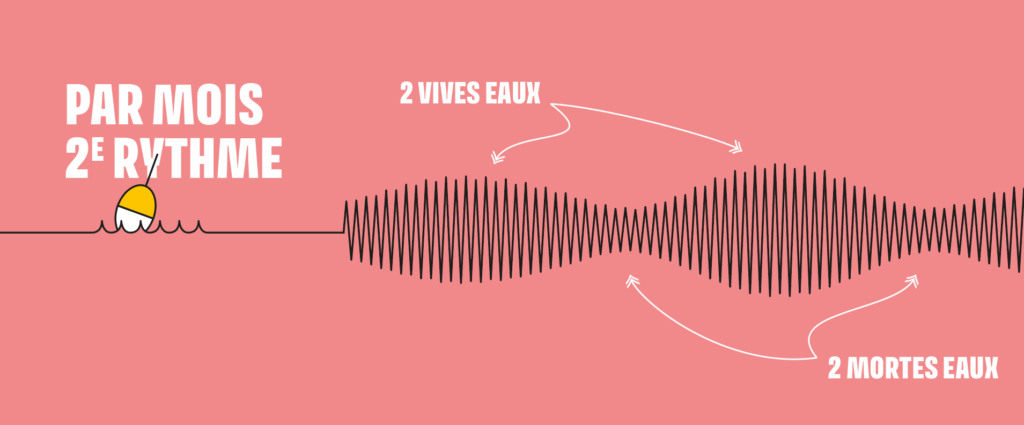
How many tidal periods per month?
This is the second tidal rhythm that can be observed along our coastline.
Neap tide periods (the water rises and falls slightly) alternate with spring tide periods (the water rises and falls more, or even significantly).
Indeed, along our coastline, the water levels are not always the same. The water rises and falls more or less depending on these periods. On a monthly scale, there are:
- 2 spring tide periods (vives eaux)
- 2 neap tide periods (mortes eaux)
This second rhythm is linked to the phases of the moon and the relative positions of the stars.
The sun plays a role:
- its influence complements that of the moon during the full moon and new moon = spring tide.
- Its influence counteracts that of the moon during the first quarter and last quarter = neap tide.
What are coefficients?
This is a French tool used only in mainland France.
Historically, in France we use coefficients calculated for each high tide. They were established for the port of Brest for use along the entire Atlantic coast, the English Channel, and the North Sea.
They provide information on the relative magnitude of the tidal range: the difference in water height between two successive tides, high and low.
The coefficient makes it easier to interpret and indicates the magnitude of the water movement.
The greater the tidal range, the higher the coefficient.
The higher the coefficient, the more the water rises and falls.
During neap tide periods with a coefficient below 45, the water rises and falls little, for example.
You can read our article about french coefficients to know more.
Coefficient scale (SHOM source)
20 – neap tides
45 – average neap tides
70 – average tides
95 – average spring tides
100 and above – high tides
120 – extraordinary equinox spring tides
Tides vary from force 1 to 6 along the coast and everywhere with the same intensity at the same time.
When are king tides?
They always occur during the spring tide period, around the time of the full or new moon.
The coefficient must be equal to or greater than 100.
The water rises significantly and retreats farther or deeper.
Here you will find all the dates of the king tides for 2025.
These dates, established for the French coast, are valid for the English, spanish or Portuguese coasts.
Other tidal rhythms
The third rhythm occurs at the equinox every six months. The spring equinox generally occurs in March, the autumn equinox in September. The sun amplifies its influence, and the coefficients are generally higher.
The fourth rhythm occurs every four years, when the equinox tides are particularly strong.
Translation : twice a year 2 equinox tides, the third rythm
Are the tides the same on the French coast?
Or English, spanish coats…
SHOM*, whose mission is to establish tidal regulations in France, has defined 23 main tidal zones, their geographical boundaries, and their main ports.
Water levels and timings vary, depending on geography, coastal profile, water depth, and wave propagation.
UKHO* en Great-Britain has the same mission…
Each tidal zone has its own calendar!
Some facts:
When the tide is low in Arcachon, it’s high in Boulogne-sur-Mer.
Water levels are twice as high in Saint-Malo as in Les Sables-d’Olonne.
The deeper the sea, the shallower the tides.
Tides are stronger in bays than in points.
The tide spreads faster if it doesn’t encounter any obstacles, as in the Bay of Biscay, and moves more slowly in the English Channel.
In the Mediterranean, tides are barely felt because the tidal range is very shallow. It’s a small, enclosed body of water.
The English Channel, a small, open, and narrow sea, is fully affected by the tides.
What is true for the French coastline is also true for the coasts of England and Spain.
Are the tides the same around the world?
No, there are several types of tides across the globe.
On our European coastline, the tides are “semi-diurnal,” with four extremes per day, our famous two high tides and two low tides per day. This is the most common type of tide in the world, occurring on 80% of the coasts.
There are so-called “diurnal” tides, with only one high tide and one low tide per day. These are rarer.
There are “semi-diurnal tides with diurnal inequalities” toward the Pacific Ocean in the USA and in the Indian Ocean.
Are tide predictions reliable?
Yes we can rely on astronomical predictions. Tidal calendars are based on astronomical forecasts, that is, the movement of the stars, whose well-oiled mechanics are reliable.
Predictions can be made over long periods of time.
However, predictions do not take into account the weather, which will ultimately have an impact. Atmospheric pressure and winds can significantly alter them.
Always check the weather conditions before beginning any maritime activity.
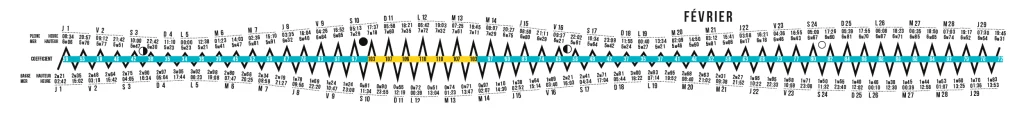
There is so much more to learn about tides. Here, we’ve gathered the basic knowledge and elements needed to read our calendar.
Our pointed curves are a graphic choice; in reality, the water remains high or low for a while, and the peaks are more “rounded.”
Our tidal calendars combine the useful with the aesthetic.
They allow you to visualize a year’s worth of tides.
The ideal tool for anticipating and planning your activities! So aim for the right tide.

Find instructions for reading our tidal calendars here.
View the map of our 2025 tidal zones.
Thank you for putting up with my translation and my poor English.
Thank you for your kindness.
Béatrice, creator of Les Marées – France Hossegor.
- * Service Hydrographique et Océanographique de la Marine
- * United Kingdom Hydrographic and Oceanic services